Table of Contents
What is Grouting?
Grouting is the process of injecting material into cavities or cracks in concrete, masonry structure, soil, rock-mass to increase the structure’s load-bearing capacity refers to grouting and the material used for this objective is called grout.
A mixture of cement, sand, and water or chemical helps to fill gaps refers to grout. It is used to repair concrete cracks, filling gaps in tiles, sealing joints and gaps filling for waterproofing and also for soil stabilization.
Grouting is also done for providing additional strength to the foundation of load-bearing structures.
Grouts are used for different applications like repairing of cracks, filling voids and gaps in tiles, sealing joints for waterproofing of the submerged structure like tunnels, canals etc. and for soil stabilization. Here we are discussing types of grout used for crack repairing.
Types of Grouting
Based on material, grouts are classified as follows:
- Cement Grouting
- Chemical Grouting
- Resin Grouting
- Bentonite Grouting
- Bituminous Grouting
Advantages of Grouting
- Grouting can be done in any ground condition.
- It doesn’t produce any vibration and can be controlled; hence there is no chance for structural damage.
- Ground structure improvement can be measured
- Suitable for limited space and low headroom application.
- Very useful for slab jacking which levels or lifts the deformed foundation.
- It can be done adjacent to an existing wall.
- It helps to control groundwater flow, seepage and hazardous waste material type and its process.
Characteristics of Grout
- Grouts are available in premixed powder form, ensuring high quality of mortar.
- It comes as one component product, only requires water and mixing, and it is ready to use.
- It possesses a shrinkage compensation property.
- There is no issue of segregation and bleeding with grout.
- It can be poured and pumped as per the need.
- It contains excellent flowing property.
- Its consistency can be adjusted
- It has suitable adhesion property with concrete.
- It has a high rate of strength development.
- It provides a highly effective bearing area.
- It is non-toxic and inflammable material.
- It possesses the non-corrosive property.
- It offers initial expansion by gas generation.
Applications Of Grouting
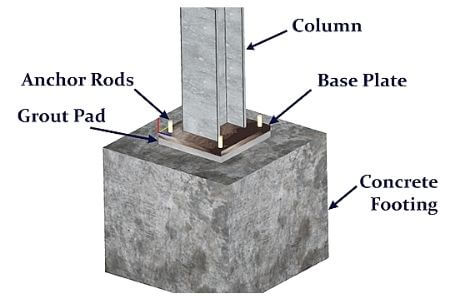
- For grouting machine foundation, base plate, bearing and column joints in precast construction.
- It is used for filling voids, gaps and cavities in the concrete.
- Grouting is done for filling the voids between the rock face and lining in tunnel work.
- It is used for fixing tendons post-tensioned in prestressed concrete construction.
- It is used for repairing pavement and ground below the foundation.
- It used for repairing cracks in concrete and defects in masonry.
- Also, for fixing ground anchors for concrete pile wall.
G1 Grout
G1 grout is mainly used for steel structures, small pumps, ships, towers and all other non-vibration machinery. Still, the precise application of the type of grout at any location should be as per the relevant drawing.
It should be cementitious, nonshrinkable, and freeflow with compressive strength equal or greater than the foundation’s concrete, but not less than 30 n/mm2 in 7 days and 40 n/mm2 in 28 days.
G2 Grout
This type of grout is generally used for prefabricated concrete structures, compressors, heavy equipment subjected to vibration and for massive structure’s column bearing plates.
The grout’s minimum compressive strength should be 50 N/mm2 in 7 days and 60 n/mm2 in 28 days. The grout’s flexible strength should exceed 9n/mm2 in 28 days.

The grout should be cementitious, non-shrinkable high strength grout example Fosroc Conbextra GP2, MC -Bauchemie Emcekrete and Sikka or similar approved by EIC. The specific location for the application of grout should be followed from the drawing.
Grouting Process
Mixing of Grout and Tools
Take the required quantity of water in a drum, put grout powder in it, and then mix it. Mixing of grouting powder can be done mechanically using an electric drill at low speed ( max 500 RPM) with water in an appropriate ratio to avoid air-entraining. For the desired consistency and flow property, the mixing ratio can be adjusted.

For Flowable Grouting – Water: Powder = 0.14 to 0.16 by weight (4.2 l to 4.8 litres water for 30 kg bag).
For Pourable Grouting – Water: Powder = 0.12 to 0.14 by weight (3.6l to 4.2 litres water for 30 kg bag).
The minimum mixing time for the mixture is 3 minutes.
Surface Preparation
Prepare the grouting surface by cleaning it through a high-pressure water jet, scrabbles, blast cleaning, etc. To ensure a saturated surface dry condition during the entire process, the concrete surface should be pre-soaked with water.
Application Process
After mixing grout, pour it immediately into the surface to be grouted. Ensure that air replaced by the grout could escape easily; otherwise, trapped air will prevent full contact grouting.
To maintain a saturated surface dry condition, wet the porous surface, especially when grouting base plates. Maintain a continuous and sufficient pressure head to keep grout flowing.
For the optimum use of the product’s expansion properties, try to use it as fast as possible(within 15 minutes).
Types of Grout used For Ceramic Tiles

- Unsanded grout: It is suitable for wall tiles that have grout joints less than 3.175 mm (1/8″) wide.
- Finely sanded grout: It is useful for floor tiles with joints 3.175 to 9.525 mm (1/8″ to 3/8″) wide.
- Quarry-type grout: It is similar to finely sanded grout for ceramic tiles, but the coarser grade sand is utilized. It is suitable for 9.525 to 12.7 mm (3/8″ to 1/2″) wide joints.
- Epoxy grout: It is made of an epoxy resin and hardener. Epoxy grout offers high resistance to stains and chemicals and possesses an excellent bonding strength. It is an ideal choice for areas susceptible to stains like countertops and others.
Also, Read
10 Best Tiles Companies In India 2021
10 Best Cement Companies In India 2021
Difference Between Ceramic Tiles and Vitrified Tiles
Pre-stressed Concrete – Definition, Methods, Advantages and Disadvantages
Difference Between Pre Tensioning and Post Tensioning
Difference Between Granite and Marble