Common taxonomy is critical to productivity, transparency, collaboration, and information re-use/management. Within the facility management where process, technology, and productivity lags, common taxonomy must be at the forefront.
Various standards are in place and evolving. Here’s a quick view of FM data standards for Europe.
EN 15221-1: Facility Management – Part 1: Terms and Definitions Version EN 15221-1:2006
This draft European standard gives relevant terms and definitions in the area of Facility Management. It also provides a structure of facility services.
EN 15221-2: Facility Management – Part 2:
Facility Management — Agreements -Guidance on how to prepare Facility Management agreements Version EN 15221-2:2006
This document is a working and standardized tool intended for parties who wish to draw up the Facility Management agreement within the European Common Market. It offers headings, which are not exhaustive. Parties may or may not include, exclude, modify and adapt these headings to their own contracts.
Definition of Facility Management – an integrated process to support and improve the effectiveness of the primary activities of an organization by the management and delivery of agreed support services for the appropriate environment that is needed to achieve its changing objectives.
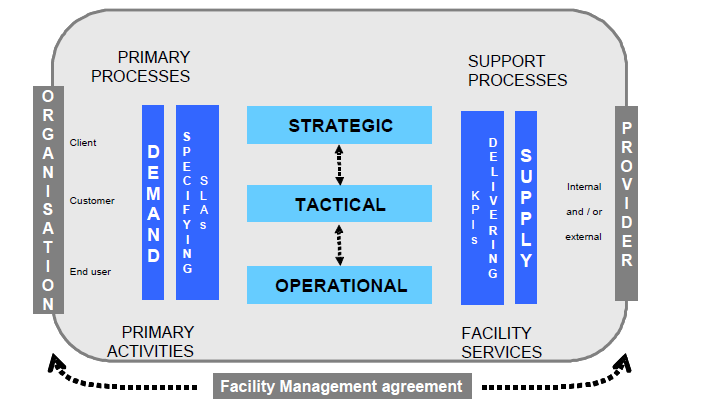
EN 15221-3: facility management – Part 3:
Guidance how to achieve/ensure quality in facility management
Provides guidance how to measure, achieve and improve quality in FM. It gives complementary guidelines to ISO 9000, ISO 9001 and EN 15221-2 within the framework of EN 15221-1.
Scope
Normative references
Terms and definitions
Basics of quality management
4.1 Importance of quality in FM
4.2 Criteria, background, elements and influences to quality
4.3 Type of characteristics
4.4 Pathway from needs to experiencing Delivery
4.5 Quality management
Process of quality management
5.1 General introduction of the process
5.2 Demand
5.3 Determining and defining requirements
5.4 Service Level (SL)
5.5 Developing measurement metrics (hierarchy of indicators)
5.6 Quality aspects by organizing delivery of fm products
5.7 Quality aspects by delivering fm products
5.8 General introduction into performance management
5.9 Measurement and calculation
5.10 Analyze deviation
5.11 Actions based on deviation
5.12 Continuous improvement
Quality:
degree to which a set of inherent characteristics fulfils requirements
Requirement:
need or expectation that is stated, generally implied or obligatory
Characteristic: distinguishing feature
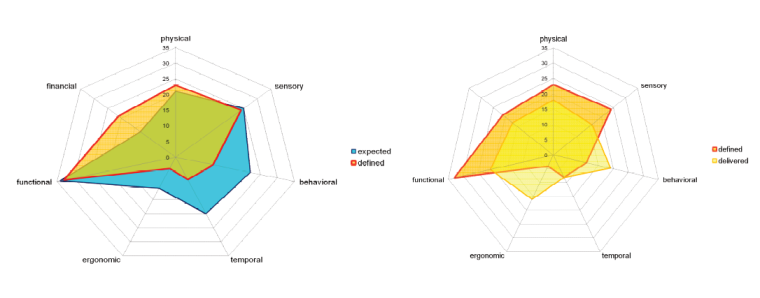
A characteristic can be inherent or assigned and can be qualitative or quantitative. There are various classes of characteristics, such as the following:
— physical (e.g. mechanical, electrical, chemical or biological characteristics);
— sensory (e.g. related to smell, touch, taste, sight, hearing);
— behavioral (e.g. courtesy, honesty, veracity);
— temporal (e.g. punctuality, reliability, availability);
— ergonomic (e.g. physiological characteristic, or related to human safety);
— functional (e.g. maximum speed of an aircraft).
Product:
result of a process
product categories, as follows:
– services (e.g. transport);
– software (e.g. computer program, dictionary);
– hardware (e.g. engine mechanical part);
grade
Category or rank given to different quality requirements for products, processes or systems having the same functional use.
service level
Complete description of requirements of a product, process or system with their characteristics.
The described set of characteristics in the SL can be graded within boundaries suitable for measurement and analysis.
indicator
Ceasured or calculated characteristic (or a set of characteristics) of a product according to a given formula, which assess the status or level of performance at defined time.
key performance indicator
Indicator that provides essential information about performance of the client´s organization.
The key performance indicators have to be given by the client´s organization, based on its strategic goals pursuing the development of the primary activities.
FM-indicator
Indicator that measures the quality of fm products.
They are used on different levels (e.g. strategic, tactical or operational Level).
FM-key performance indicator (fm kpi)
Indicator directly impacting the primary activities and the objectives of the client´s organisation.
Fm-indicator linked to client’s organisation objectives and related product which directly impacts the primary activities.
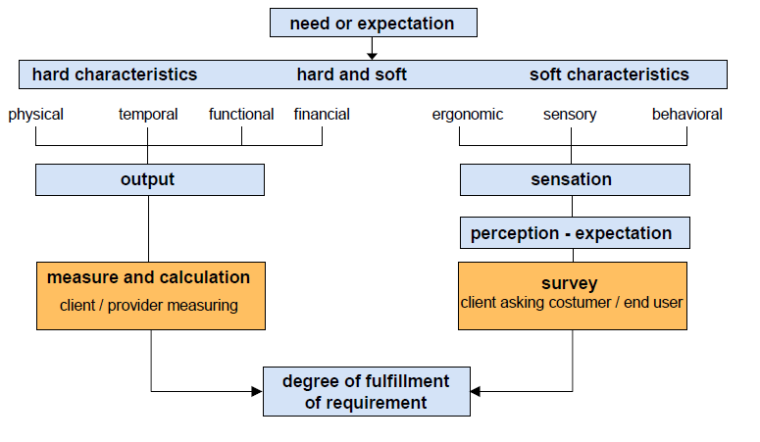
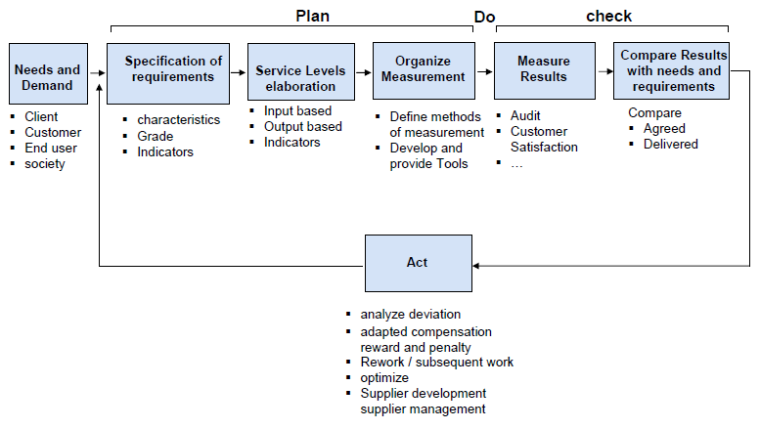
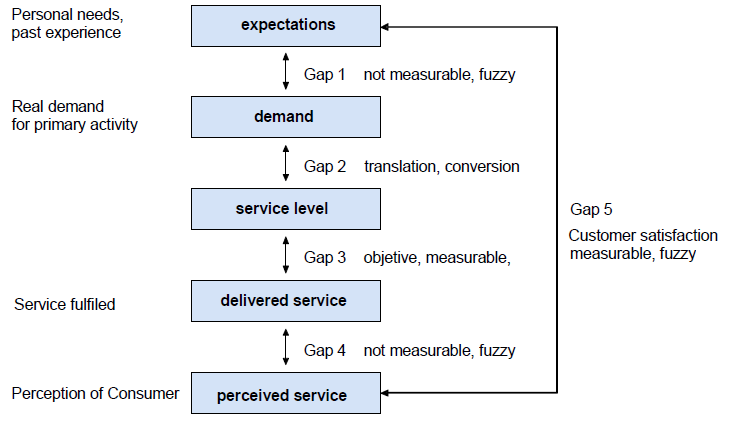
EN 15221-4: facility management – Part 4: Taxonomy of facility management
Focused on the concept of classified facility products / services by defining relevant interrelationship of service elements and their hierarchical structures, associated terms and cost allocation
EN 15221-5: facility management – Part 5:
Guidance on the development and improvement of processes
Provides guidance to FM organizations on the development and improvement of their processes to support the primary activities.
EN 15221-6: facility management – Part 6:
Space measurement
Area and space measurement for existing buildings
via http://www.4Click,s.com – premier software for cost estimating and efficient project delivery methods and management – JOC, SABER, IDIQ, IPD, SATOC, MATOC, MACC, POCA, BOA ….

