(Source:A report for the Government Construction Client Group Building Information Modelling (BIM) Working Party Strategy Paper March 2011)
via http://www.4Clicks.com – Premier technology solutions for cost estimating and efficient project delivery method implementation – JOC, SABER, IPD, IDIQ, SATOC, MATOC, MACC, POCA, BOA …
What is COBie?
COBie is a vehicle for sharing predominantly non-graphic data about a facility. The primary motivation for the use of COBie is to ensure that the Client as Owner, Operator and Occupier receives the information about the facility in as complete and as useful form as possible. Wherever possible, data should be recorded within COBie. The COBie dataset can additionally act as a guided index to the supplementary documentation, including 2D and 3D information.
COBie2 was created to provide a means for the faculties industry to communicate information about facilities so that the client can immediately take full and responsible ownership. It arose from the collaboration of the US Department of State, US Army Corps of Engineers, NASA, and the Veterans Association. In 2008 it was revised as COBie to ensure that it was relevant to facilities worldwide and was fully compatible with international standards for data and classification. Adopters of the COBie approach also include public and private owners, University of Indiana, University Southern California, in the UK Vinci Construction Ltd, and in Germany, The State of Bavaria.
COBie is a non-proprietary format based on a multiple page spread sheet. It is designed to be easily managed by organisations of any size and at any level of IT capability, allowing each of them to contribute efficiently to a single representation of the asset. It requires only information that is (or should be) available anyway, so it does not represent a change in the expected content, only in its usefulness and accessibility. The intent is to not create information that is not already available or produced as part of the existing processes. The aim is to structure and rationalise the information for re-purposing and use downstream. COBie also acts as an index to other documents. Overall COBie provides traceability and visibility of design, construction and handover decisions to all supply and client side stakeholders.
COBie is used for communication, as a means of information exchange between parties, particularly to the customer. Where automation is not in use, such as in the lower tiers of the supply chain, COBie information can be captured using direct entry into the spread sheet, often using cut-and-paste from existing schedules and documents. Parties including the client can use the COBie format as a primary document for managing the asset. Design development, construction management and asset management applications have had no difficulty in interfacing with the format.
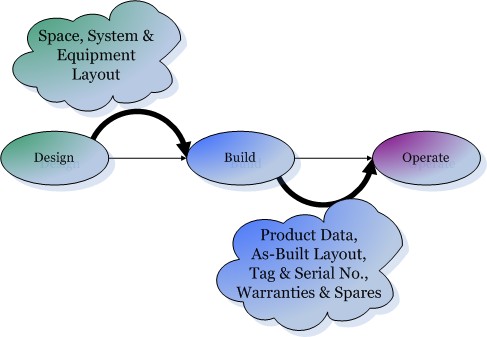
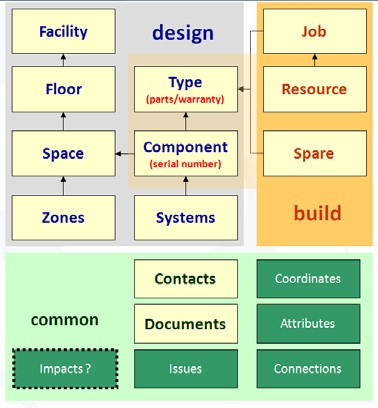
COBie comprises sheets that document the facility, the levels (or sectors), spaces and zones that make up the function of the facility. These are then filled with the actual manageable systems and assets and details of their product types. During construction and installation these are amplified with information about the spares, warranties, and maintenance requirements. Throughout the process additional attributes, issues and documents can be associated to all these items.
2 COBie (Construction Operations Building information exchange) was developed by a number of US public agencies to improve the handover process to building owner-operators.
COBie data is accumulated throughout the life cycle
COBie transfers the information needed by the owner/operator to manage their asset efficiently. The principal use-case is therefore the handover of a facility after commissioning of the owner/operator. Typical questions answered by COBie include:
- What is the design performance of my asset? Energy, rental, quality measures,
- What is the amount of floor space of estate? Classified by building type.
- What is the occupancy level of my estate/per building?
- What is the required plant and equipment maintenance scheduling – preventative and reactive?
- What is my operational cost expected to be?
- What is my as-designed energy use cost expected to be? What is my actual energy use? The use of
1. The handover of a facility to the owner/operator.
2. The capture of commissioning and survey information.
3. The reporting of the designed project ready for tendering.
4. The coordination of maintenance records of existing infrastructure.
5. The documentation of issues discovered throughout the life cycle.
6. The delivery of product data.
7. The reporting of design intent at the early design stage.
8. The comparison of briefing requirements against the designed and as built
COBie documents the asset in 16 consistent and linked sheets
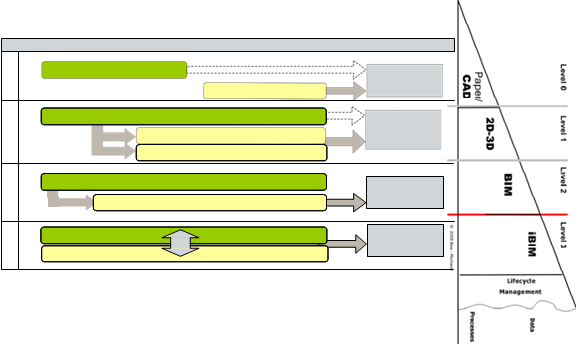
We anticipate that our application of COBie will develop as the various technologies in the market mature, broadly in line with our “maturity levels model” described in appendix 3. For the majority of the five years of the life of this strategy we anticipate that most of the market will be engaged in or around level 2. For all deliveries at this level, COBie will be adequate as a transport mechanism but may well require additional development to cope with additional attached data, which some clients may start to wish for collection. There will also be a need to have a more robust system for processing the information as our understanding and needs grow. For this reason we have identified a stage where we would hold all delivered data in a database to enable these processes. This will need additional guidance as there would be a need to synchronise data, COBie, calculations and proprietary information at the same point in time.