1. Robust, collaborative construction delivery methods – IPD, Integrated Project Delivery, JOC – Job Order Contracting, et al . Collaboration in the building industry requires the integration of complex inter-related workflows whereby multitude of stakeholders are incorporated into a common pool of information, decision-support, and activities over an extensive period of time.
2. Standardized “Glossary”.. terms, acronyms, definitions.
3. Benchmarks, metrics.
4. Life-cycle perspective and management techniques/processes… vs. a “first cost mentality”.
5. Technology focused upon enabling robust processes…vs. current focus upon 3D modeling. Embedding vetted processes with technology enables consistent, scalable deployment.
6. Current examples of “open’ and standardized knowledge domains, processes, terms, and technologies.
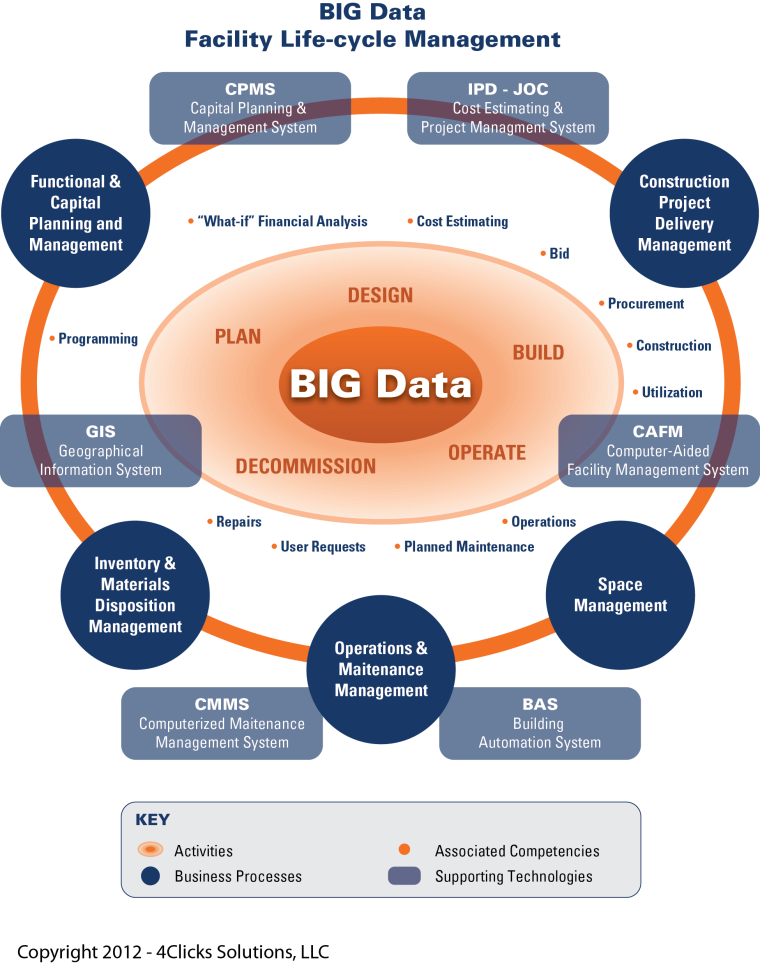
Capital planning and management systems (CPMS) – physical and functional condition monitoring and associated capital reinvestment planning. traditionally dealing with expenditures in excess of $10,000.
Computerized Maintenance Management systems (CMMS) – inventory, repair, maintenance of ‘movable equipment’. Typically involving expenditures of $10,000 or less.
Computer-Aid Facility Managements Systems (CAFM) – space planning, move management, space utilization.
Building Automation Systems (BAS) – security, life/safety, access control, environment systems management.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) – computerized location management / positioning.
Create, read, update, delete) operations (CRUD)
Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) – structure enabling native storage of instance models
Simple Object Access Protocol, is a protocol specification for exchanging structured information in the implementation of Web Services in computer networks.
Representational State Transfer (REST) is an architectural style for large-scale software design
Construction Operations Building Information Exchange (COBie) a specification used in the handover of Facility Management information.
OMNICLASS in simple terms, a standard for organizing all construction information. The concept for OmniClass is derived from internationally-accepted standards that have been developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Construction Information Society (ICIS) subcommittees and workgroups from the early-1990s to the present.
ISO Technical Committee 59, Subcommittee 13, Working Group 2 (TC59/SC13/WG2) drafted a standard for a classification framework (ISO 12006-2, more information below) based on traditional classification but also recognized an alternative “object oriented” approach, which had to be explored further.
UniFormat is a standard for classifying building specifications, cost estimating, and cost analysis in the U.S. and Canada.
MasterFormat is a standard for organizing specifications and other written information for commercial and institutional building projects in the U.S. and Canada.